Understanding Psoriasis: A Comprehensive Overview Provided by Epicorium Skin Clinic
Table of Contents
Psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune disease, triggers an overactive immune response leading to the rapid multiplication of skin cells. This results in the development of scaly and inflamed patches on various parts of the body, such as the scalp, elbows, and knees. While the exact cause of psoriasis remains uncertain, a combination of genetic and environmental factors contributes to its onset. Epicorium Skin Clinic is dedicated to providing thorough insights on psoriasis and effective management techniques to alleviate its symptoms.
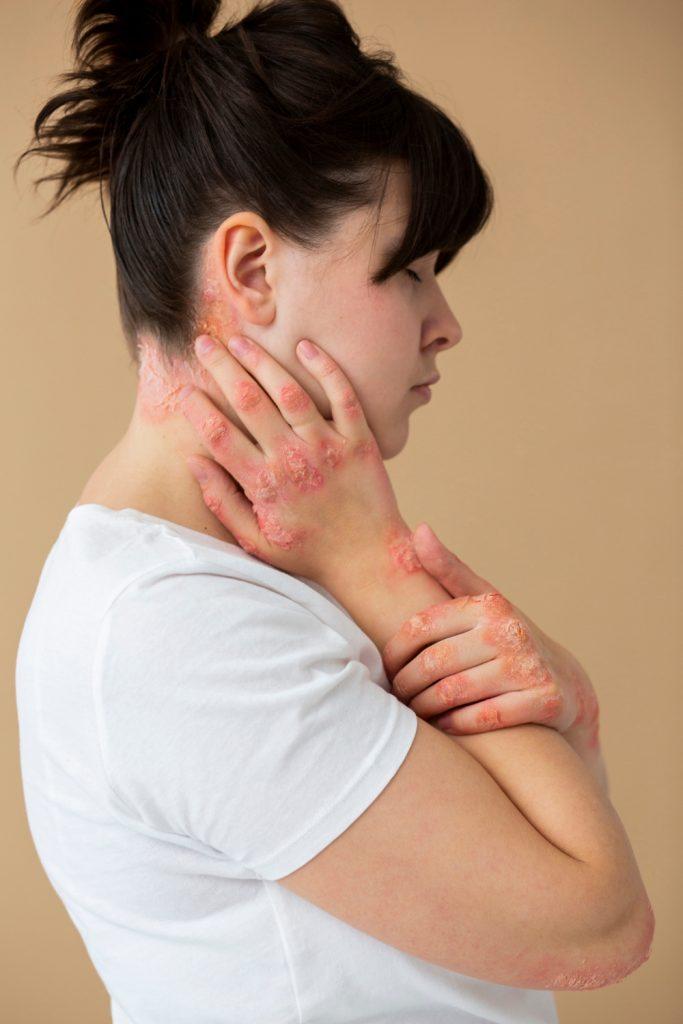
Understanding Psoriasis:
Psoriasis can manifest differently in individuals and may undergo cycles of exacerbation followed by remission. The severity and type of psoriasis play a crucial role in determining the appropriate treatment approach. While mild psoriasis can be effectively managed using topical creams or ointments, moderate to severe cases may require medications, injections, or light therapies. Furthermore, identifying and managing triggers, such as stress and skin injuries, can significantly help in controlling symptoms.
Associated Health Risks:
People living with psoriasis face an increased risk of developing various serious conditions, including psoriatic arthritis, cardiovascular events like heart attacks and strokes, mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression, Crohn’s disease, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, obesity, osteoporosis, uveitis, liver disease, and kidney disease.
Prevalence of Psoriasis:
While psoriasis can affect anyone, it is more commonly observed in adults than in children. Both men and women are equally susceptible to this condition.
Types of Psoriasis:
Psoriasis manifests in different forms, including:
- Plaque Psoriasis: This is the most prevalent type, characterized by raised, red patches of skin covered in silvery-white scales. These patches usually appear symmetrically on the scalp, trunk, and limbs, especially the elbows and knees.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Often found in children or young adults, guttate psoriasis appears as small, red dots on the torso or limbs. It is frequently triggered by upper respiratory tract infections, such as sore throat.
- Pustular Psoriasis: In this form, red skin surrounds pus-filled bumps called pustules. Pustular psoriasis commonly affects the hands and feet, but can also cover larger areas of the body. Factors like medications, infections, stress, or certain chemicals can trigger its symptoms. It is a dermatological emergency that needs immediate medical attention.
- Inverse Psoriasis: This type appears as smooth, red patches in skin folds, such as beneath the breasts or in the groin or armpits. Increased friction and sweating can worsen its effects.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: Although rare, this severe form of psoriasis involves red, scaly skin covering most of the body. Erythrodermic psoriasis can be triggered by severe sunburns or certain medications. It tends to develop in individuals who already have a different type of psoriasis that is not well controlled, making it significantly more serious. This too requires immediate medical attention.
Symptoms of Psoriasis:
Symptoms of psoriasis may vary from person to person but often include:
- Thick, red patches of skin covered in silvery-white scales that itch or burn. These commonly occur on the elbows, knees, scalp, trunk, palms, and soles of the feet. On scratch or rub, white silvery scales fall like the wax falling while scraping the candle.
- Dry and cracked skin that may cause discomfort through itching or even minor bleeding.
- Thickened, ridged, and pitted nails.
- Sleep disturbances affecting overall quality.
- Dandruff like scaling overhead, but scales are thick and adherent to the scalp.
Psoriatic Arthritis:
Some individuals with psoriasis may also develop psoriatic arthritis, which presents with symptoms such as joint stiffness, swelling, pain, neck or back discomfort, and Achilles heel pain. Timely medical attention is crucial to prevent irreversible damage caused by untreated psoriatic arthritis.
Causes of Psoriasis:
Psoriasis is classified as an immune-mediated disease, resulting from an overactive immune response. Immune cells become active and produce molecules that accelerate skin cell production, leading to inflammation and scaling. Researchers believe genetics and environmental factors contribute to faulty immune cell activation. Genetic studies have identified certain genes associated with immune system functioning. External factors, including infections like streptococcal and HIV infections, certain medications, smoking, and obesity, may increase the risk of developing psoriasis.
Diagnosis of Psoriasis:
Diagnosing psoriasis typically involves a thorough examination of the skin, scalp, and nails by a dermatologist. Medical professionals may also inquire about symptoms, recent illnesses, severe stress, medication usage, family history, and joint tenderness. In certain cases, a small skin sample may be obtained for microscopic analysis to rule out other skin conditions resembling psoriasis.
Treatment Approaches:
While no cure for psoriasis currently exists, various treatments are available to effectively manage symptoms and improve quality of life. The most suitable treatment option is determined by evaluating the type and severity of psoriasis, its location on the body, and potential medication side effects. Treatment approaches include:
Medications:
- Topical therapies, such as corticosteroid-based creams, vitamin D derivatives, retinoids, coal tar, PDE4 inhibitors, and AhR-activating medications.
- Methotrexate, which suppresses the immune system.
- Oral retinoids for moderate to severe cases are often used in combination with phototherapy.
- Biologic response modifiers that block immune molecules contributing to inflammation.
- Immunosuppressants are used for severe cases, suppressing the immune system.
- Oral PDE4 inhibitors reduce rapid cell turnover and inflammation.
- Oral TYK2 inhibitors block the activation of specific immune cells.
- The real breakthrough in psoriasis treatment is the introduction of biologics in injectable form achieving almost 90 to 100% results.
Phototherapy:
Phototherapy involves exposing the affected skin to controlled doses of ultraviolet light either in a clinical setting or using a prescribed home unit. It is ideal for treating widespread psoriasis.
Collaborative Care:
Psoriasis treatment involves a multidisciplinary approach, with dermatologists leading the treatment plan. Rheumatologists specialize in managing psoriatic arthritis, while mental health professionals provide counseling for associated mental health disorders. Primary healthcare providers play a crucial role in overall care, working alongside dermatologists and other specialists.
Living with Psoriasis:
Living with psoriasis can impact daily life, including work and sleep patterns. Nevertheless, healthcare providers and support systems can aid in reducing symptoms. Consider the following to manage symptoms effectively:
- Keep the skin well-moisturized using mild soap with added oils after bathing.
- Maintain a healthy weight, as obesity can aggravate psoriasis symptoms.
- Adopt a healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean diet, known to aid in managing psoriasis.
- Collaborate with doctors to create a cessation plan if you currently smoke, as smoking tends to worsen symptoms.
- Limit alcohol consumption, as excessive intake may worsen symptoms.
- Moderate sun exposure can be beneficial, but it is important to consult a doctor for guidance to avoid exacerbation of symptoms.
- Identify and avoid known triggers, such as stress, cold weather, skin injuries, specific medications, and infections.
- Join support groups or seek the assistance of mental health professionals to cope with the emotional impact of the condition.
In conclusion, psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune disease, requires holistic management targeting both physical and mental well-being. By understanding the different types, symptoms, causes, and available treatment options, individuals can effectively control psoriasis and enhance their quality of life. With the advent of biologics, psoriasis patients can dream of “clear skin”, which is a reality nowadays. Epicorium Skin Clinic aims to provide comprehensive support to those affected by psoriasis through its expertise, research, and patient-centric approach.