Chemical Cautery – How Does It Work, Uses, And Treatments Involved
Chemical cautery procedures involve the treatment of diseased tissue with the help of a cauterizing agent.
We at Epicorium, offer a seamless Chemical Cautery Treatment or Cauterization for various skin concerns like warts, skin tags, wounds, tumors, and eye disease. A dermatologist usually performs Chemical Cautery Treatment using electricity or chemicals to burn the tissue. If you are looking for an excellent Chemical Cautery Treatment experience, get in touch with our team.
How does chemical cautery work?
Read MoreChemical Cautery – How Does It Work, Uses, And Treatments Involved
Chemical cautery procedures involve the treatment of diseased tissue with the help of a cauterizing agent.
We at Epicorium, offer a seamless Chemical Cautery Treatment or Cauterization for various skin concerns like warts, skin tags, wounds, tumors, and eye disease. A dermatologist usually performs Chemical Cautery Treatment using electricity or chemicals to burn the tissue. If you are looking for an excellent Chemical Cautery Treatment experience, get in touch with our team.
How does chemical cautery work?
In this procedure, the chemical required for the treatment is applied to the treatment area by the dermatologist. This causes necrosis. This means, that the tissue in the affected area dies. The healing mechanism is triggered and the healthy tissues get regenerated.
Where is chemical cautery used?
Chemical cautery is used for the treatments like milia, warts, skin tags, ingrown toe nail, and some more conditions like
- Molluscum Contagiosm
- Xanthelasma Palpebraum
- Blood Loss During A Surgery
- Blood Loss During Chronic Nosebleeds
- Tumour removal
- Blood Loss After An Injury
- Eye Disease Management
Chemical Cautery for warts and skin tags
Commonly, there are two types of warts which can be treated using chemical cautery method:
One is plane wart and the other one is common warts.
Plane warts: These are the warts that are plane, flat skin-colored lesions. In this procedure, the chemical cautery just touches the lesion surface and in such a way that it does not spread beyond the lesion margins.
Common warts: Most commonly, these types of warts are removed with the help of RFA radio frequency, but sometimes during lesions that are very small, they can be treated with chemical cautery as well.
Even skin tags can be removed with the help of chemical cautery. The chemical agent that is used in the skin tag removal is applied at the base.
Nasal Cauterisation
There are additional processes performed for nasal cauterisation. This is due to the nasal passageway’s limited capability during therapy. The operation begins with intranasal anaesthetic, which is followed by a vasoconstricting drug to help relieve congestion. After that, the cauterising chemical is applied twice. Following the treatment, the doctor will apply medication to the nasal tissues to comfort them. To reap long-term advantages, the treatment should be repeated several times.
What are the commonly used chemical agents in chemical cautery?
The commonly used chemical cautery agents are:
TCA (Trichloroacetic acid): Different concentrations of TCA like 25%, 50%, 75% or 100% are used at different treatment sites and lesion types. The higher the percentage, the higher is the strength of the chemical agent.
The other type of chemical agent used is called carbolic acid or phenol
How does chemical cautery treatment works?
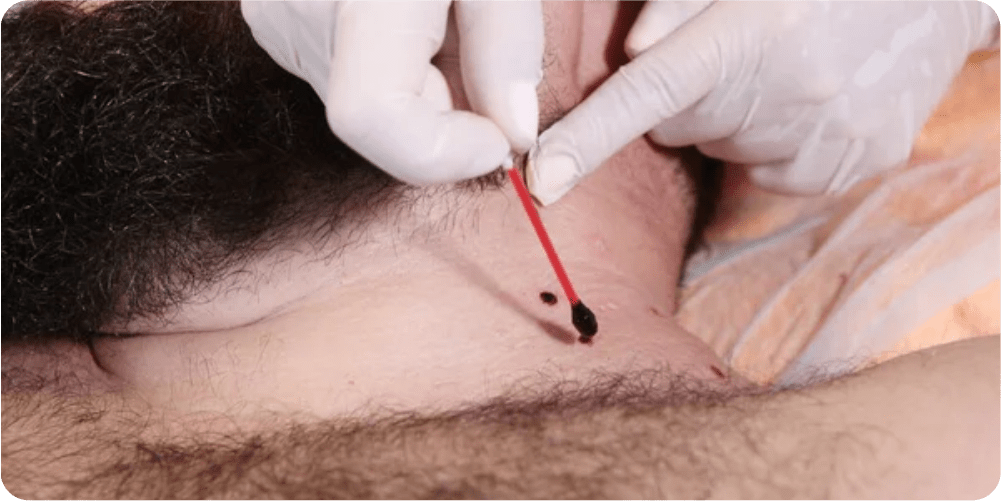
The area to be treated is first cleaned, and then the dermatologist applies the chemical agent on the skin lesion. There will be a burning sensation in the first few seconds. The agent will be applied with the help of needle, ear bud, tooth pick, or cotton sticks depending upon the lesion size. After applying the agent, a white frosting will begin to appear. This indicates that the action of therapy has started.
Now after a few hours, the white frosting will disappear. Mild swelling and redness might appear for a day. This is typically due to the formation of scab at the application site. The scab usually falls off in a week or so. The person undergoing this treatment is usually advised to keep the wound clean for further preventing the infection. They are also advised to use topical antibacterial cream. This procedure in major cases does not leave any scar on the treatment site.
Chemical Cautery Treatment At Epicorium
A simple chemical cauterization process at our center takes roughly 30 minutes. For larger wounds or scars, surgery may take longer, but most patients can return to routine the same day.
We start with the inspection of the infected area followed by a blood test. A blood test is performed to detect anti-clotting factors and anemia. Anemia is required in Chemical Cautery Treatment to avoid pain during surgery. And, in order to do so, we have the best anaesthetic available at all of our locations. After the anaesthesia comes into effect, the doctor burns off the rough flesh, nasal tissue, or fistula with a stick covered with a chemical cauterizing substance, such as silver nitrate, on the treatment areas.
When the chemical reacts with the tissue, the blood vessels melt and fuse together. This stops the bleeding and eliminates the extra damaged tissue. It also seals off the regular skin surface, reducing the possibility of infection. Following the procedure, the doctor applies silver nitrate to the treatment spot to prevent further granulation tissue expansion.
Dermatologists advise not to go for this procedure in following cases:
Chemical cautery shouldn’t be used when:
- The lesion size is very large
- The treatment site has active infection
- If the patient undergoing the treatment has the chances of developing keloids
FAQs
The side effects associated with chemical cautery usually fade away in a few days and are temporary. These are some of its adverse effects:
Irritation and burning
Swelling in the area
Infection if the wound is not properly kept clean
That instant white icing fades away after a few hours. Redness and minor swelling may last for 24 hours. There is scab formation at the application site. Scabs after cauterization normally fall off in 7-10 days. To minimise subsequent infection, patients should maintain the chemical cautery incision clean and may need to apply topical antibiotic cream. Healing after cauterization is typically uneventful and leaves no scar at the location.
You will have a detailed consultation with the best dermatologist, Dr. Namitha Chathra.
Your treatment regimen will be customised to your needs and convivence.
All the treatments are conducted by Dr. Namitha Chathra and his well-trained team, under strict guidelines and protocols to ensure your safety.
Ensured results of chemical cautery treatment
Personalized post procedure care